Before installing Exchange Server, it’s good to know the Exchange database best practices. Design first and from there on you can configure a great Exchange configuration. For example, how many databases should you configure on a volume? Can you keep the database and log folder on the same disk?
It’s important to know what kind of Exchange configurations there are and from there a decision can be made. In this article, you will learn how how to design Exchange database best practices.
Exchange Server architecture
There are two Exchange architectures:
- Standalone – One single Exchange Server
- High Availability (DAG) – Multiple Exchange Servers
I recommend installing Exchange Server in High Availability. If one Exchange Server stops working for any reason, the mail flow will keep going on. This will give you time to fix the broken Exchange Server, without the users notifying problems.
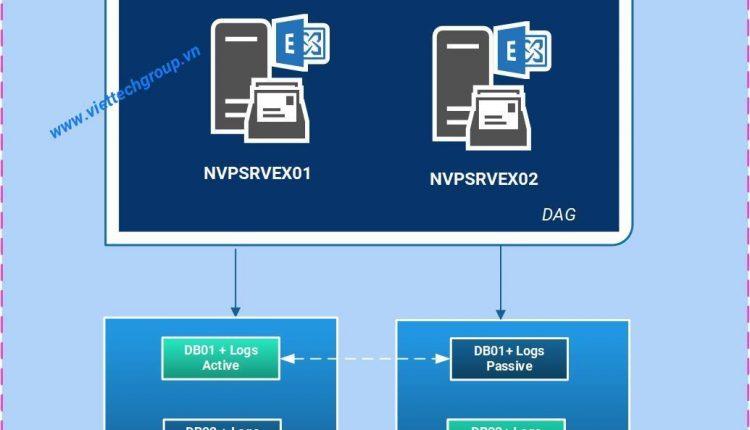
Standalone Exchange Server
- Single database per volume is recommended
- Single log per volume is recommended
- Both the same database and log (co-location) on a volume is not supported
- Database size of 200GB per database or less
- Windows basic disk type
- GPT partitions instead of MBR
- Configure volumes as mount points and not drive letters is recommended
- Configure volumes for database and log as ReFS or NTFS
- Allocation unit size of 64KB for both database and log volumes
- Start the naming convention of the database with DB01 and keep increasing the number
For recoverability, move database (.edb) file and logs from the same database to different volumes backed by different physical disks.
High Availability Exchange Servers
- Single database per volume is supported, is not required
- Single log per volume is supported, is not required
- Both the same database and log (co-location) is supported
- The number of databases per volume should be equal to the number of copies of each database
- Database size of 2000GB per database or less
- Windows basic disk type
- GPT Partitions instead of MBR
- Configure volumes as mount points and not drive letters is recommended
- Configure volumes for database and log as ReFS or NTFS
- Allocation unit size of 64KB for both database and log volumes
- Start the naming convention of the database with DB01 and keep increasing the number
GPT is a disk architecture that expands on the older master boot record (MBR) partitioning scheme. GPT maximum formatted partition size is 256 terabytes. MBR maximum formatted partition size is 2 terabytes.
Exchange database examples
A couple of examples that will show the best practices for Exchange databases in a standalone or high availability architecture:
Example 1. You want to configure a standalone Exchange Server in the organization. Place the database on a separate volume and place the log on a separate volume. Don’t add more than one database per volume and one log per volume. Both volumes backed by different physical disks.
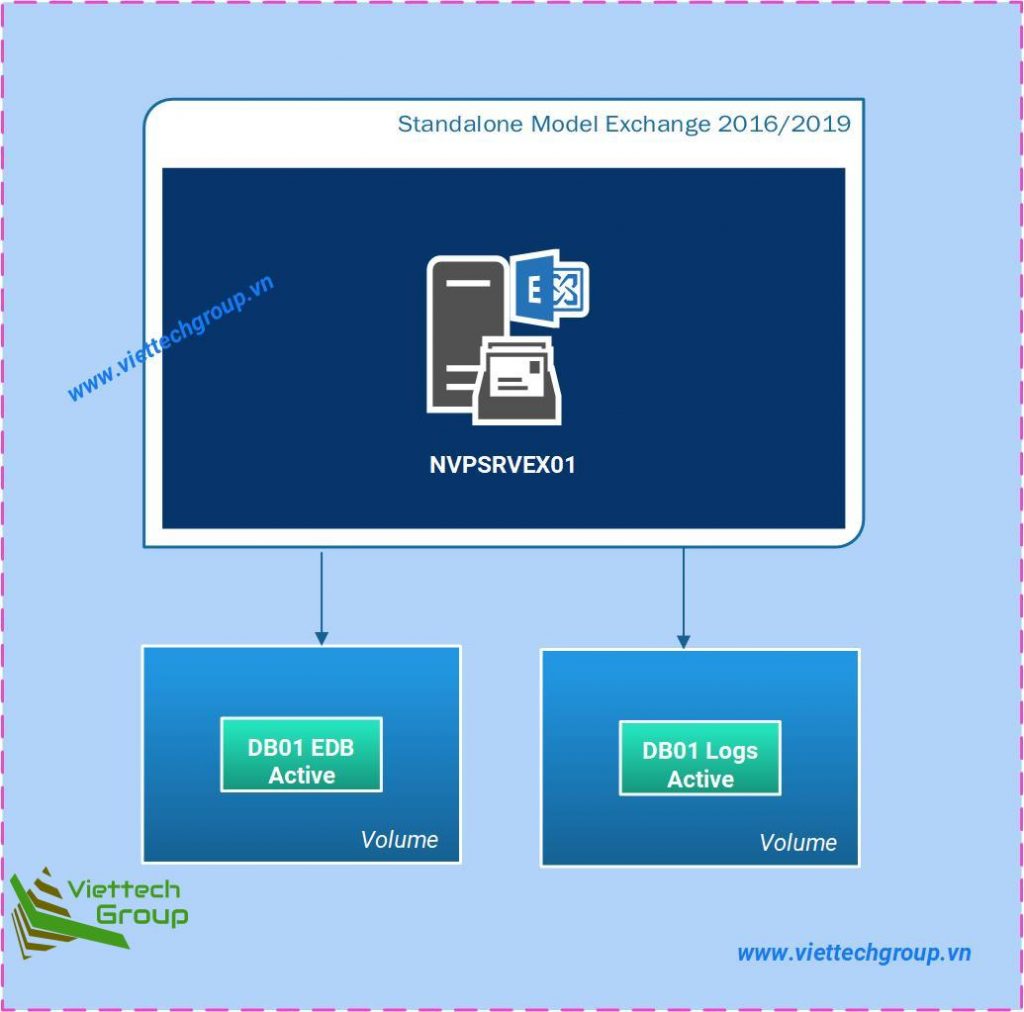
Example 2. If you have a DAG configured with two Exchange Servers. Place the database and log on the same volume. Not more than two databases and two logs (co-location) on the same volume. Both volumes backed by different physical disks.
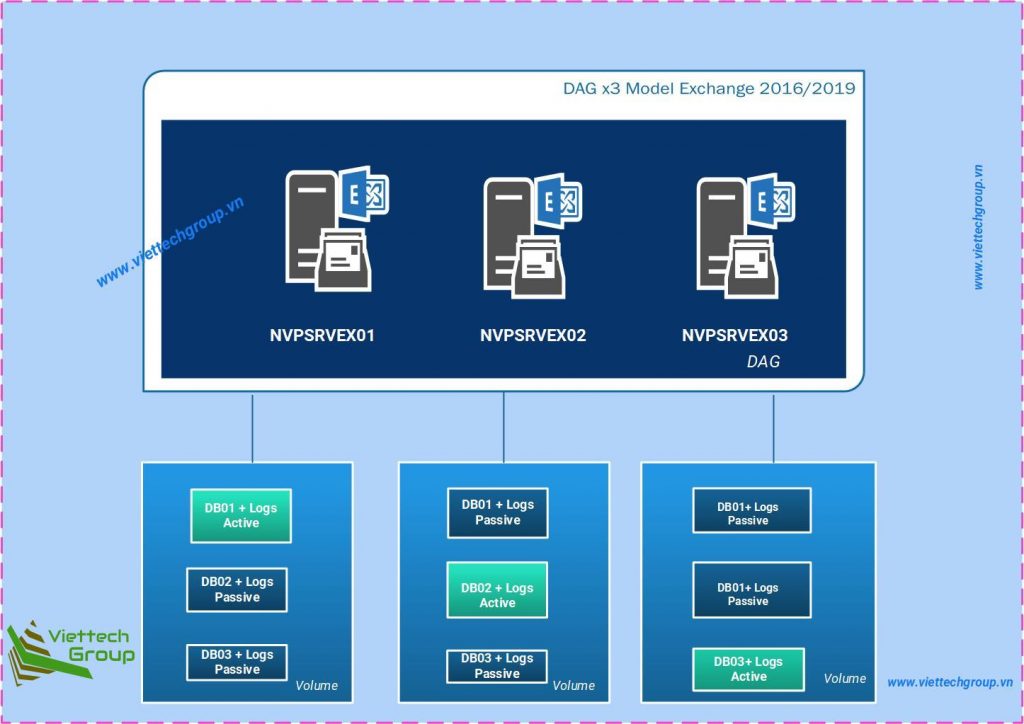
Example 3. If you have a DAG configured with three Exchange Servers. Place the database and log on the same volume. Not more than three databases and three logs (co-location) on the same volume. All three volumes backed by different physical disks.
Example 4. The configuration in the diagram shows four servers. All four servers have the same four databases all hosted on a single disk per server. The number of database copies configured per volume should be equal to the number of copies of each database. For example, if you have four copies of your databases, you should use four database copies per volume.
I hope that the article Exchange database best practices helped you in designing the Exchange environment.
Keep reading: Exchange database size recommendations »
Conclusion
In this article, you learned the Exchange database best practices. The next step is to configure ReFS volume in Exchange Server. Did you enjoy this article? You may also like the article Create mailbox database Exchange 2016. Don’t forget to follow us and share this article.