Review Active Directory Components
Review Active Directory Components
Review Active Directory Components
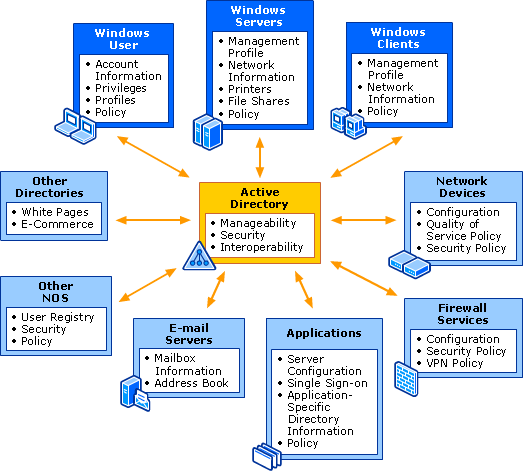
You can use a variety of Active Directory components to define the directory structure. These components exist in the physical and logical layers of the organization. The physical layer components control how the directory information is structured and stored. The logical layer components, however, control how users and administrators view information and also control access to information. Note that the physical and logical layers are completely separate .
The physical components of Active Directory ( physical )
The physical components of the Active Directory are sites and subnets . A site is a combination of one or more IP subnets that are connected to very secure links. A subnet is a group of network IP addresses . You use sites and subnets for directory structure to reflect the physical structure of your organization. You use sites to map the physical structure of your network. As shown in Figure 4-5 , a site usually has the same boundaries that your LANs have. Since mapping the siteSeparate and independent of the logical components logical directory, they do not need a network connection between physical structures and logical structures are in the directory .
While sites can have multiple IP address ranges , each subnet has a specific IP address range . The subnet name is displayed via network / bitsmask , such as 24 / 10.1.11.0 where 10.1.11.0 relates to a network address and 255.255.255.0 to a network mask that are combined and named 24 / 10.1.11.0 Is. Figure 6-1 shows the subnets of several networks. For example, St. Paul has subnets 24 / 10.1.11.0 and 24 / 10.1.12.0 is .
Figure 4-5 mapping the subnets to the network structure
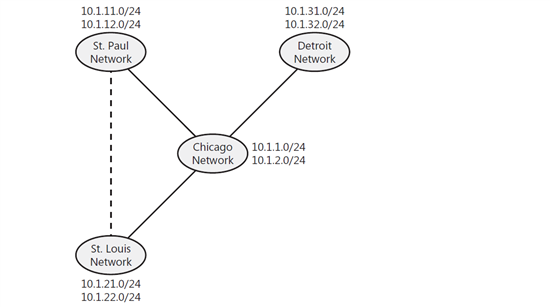
Figure 4-5 Local area network LANs within a WAN and related subnets
Ideally, when several subnets are on sites , you need to make sure all subnets are properly connected . The purpose of a good connection is to ensure that the subnets are connected by fast, reliable connections. The fast connections which is generally at least 512 kilobits per second kbps and have a reliable network connection that is always active and bandwidth bandwidth available for communications network directory traffic is most of the times .
In the picture, the Detroit and St. Louis networks are shown in Figure 4-5 . Louis is connected to the Chicago network using a 2 kbps kbps connection, so they are well connected. For this reason, all 5 networks can be part of a site . Network St. Paul connects 2 kbps to the Chicago network and 1 kbps to the St. Louis network Louis is connected. That’s why St. Paul is not well connected and should not be part of the same site as other networks.
Figure 4-5 Internal LANs in a WAN and the associated connection speeds
When you search Active Directory, you logical components logical rather than physical components of physical ‘ll see. The reason is that sites and subnets are not part of the normal Active Directory namespace namespace . Sites only include computer objects and connection objects . These objects are used to regulate replication operations between sites . Computers to sites based on locations location in a subnet or set of subnets are assigned .
As an administrator, you need to create sites and subnets appropriate to your organization . You have to optimize authentication and replication second controller within the sites put .
The logical components of Active Directory logical
Logical components in Active Directory are domains , domain trees , domain forests and organizational units – Ous . These components help you organize resources into a logical structure. This logical structure is what is presented to users .
Domains
The second domains are the logical grouping of objects that are shared in the directory database. In a directory, domains are like a container for objects . Within a second, you can account accounts for users users , groups, groups , and computers computers and shared resources such as printers for printers and folders folders you create .
In Figure 1-4, a domain is shown as a large triangle and the objects in it are shown. The second can store millions of objects and is the parent object for all objects . Keep in mind, however, that a domain stores the information about the objects it owns and that access to those objects is controlled by security permissions . Security permissions to objects is assigned to a user determine which user access to objects , and the type of access the user is.
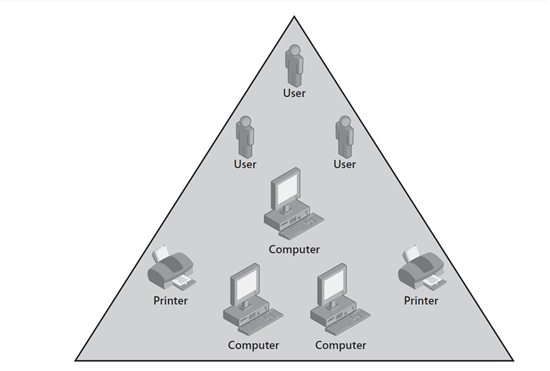
Figure 2-4 A Second Active Directory
A directory can contain one or more domains . Each domain name or domain name must be unique. If the domain is part of a private network, the new domain name you want to assign should not be incompatible with other domains on the private network. If the domain is part of the public Internet, the domain name assigned to the new domain should not be incompatible with existing domains across the Internet . That’s why you need to register your public domain name before use. You can view information on the site atInterNIC find .
Because a domain can be wider than one physical location (in multiple locations), a domain can be wider than one or more sites . A single site can also have multiple domain resources . Each domain has its own security policies and settings .
Domain functions are restricted and controlled by domain functional levels . There are several domain functional levels , including :
Windows 2000 Native, which supports Windows Server 7 and later.
Windows Server 2003, which supports Windows Server 7 and later.
Windows Server 2008, which supports Windows Server 7 and later.
(Note: Windows Server 2008 R2 is also)
You when the first domain controller in a domain New’ll install, domain functional level you set. You can raise the domain functional level , but you can’t bring it down (you can only do this on Windows Server 2008 R2 , which has its limitations). In the second chapter we will talk about domain functional levels .
Domain TREES in Active Directory
Although domains are important blocks in building Active Directory structures, they are not just directory structure blocks. Other important blocks are the domain tree structure . domain trees logical grouping of domain are .
Note : Within a directory, the tree structurerepresents a hierarchy of objects , representing parent-child relationshipsbetween objects . The domain at the top of a tree is called the root domain . The root domain is the first domain to be created in a new directory and is the parent for other domains in the domain trees . Other domain that you create the child domain known .
As an administrator, you create domain trees to reflect the structure of your organization. Domains inside a tree are shared or connected namespaces. The domain name for a child domain is that the parent domain name is added to the child domain name . In Figure 1-4 cpandl.com is the parent for tech.cpandl.com and sales.cpandl.com . tech.cpandl.com has two subdomains called eng.tech.cpandl.com and dev.tech.cpandl.com is. This makes the tech.cpandl.com for eng.tech.cpandl.com and dev.tech.cpandl.com as a parent is .
FORESTS in Active Directory
domain forests are logical groups of domain trees . Domain trees in a domain forest are separate and independent. As such, domain trees , which are part of a domain forest , do not share a batch name space . In fact, when you add a new domain to the Active Directory that is part of a separate namespace (it has a separate name), this domain is added to the forest as a new tree . For example, if the Active Directory has a single tree , as you can see in Figure 1-4, and you have a new domain calledWhen you add adatum.com to the directory, this domain is added to the forest as part of a new tree , as you can see in Figure 1-4. This domain is now recognized as the root domain for the new tree .
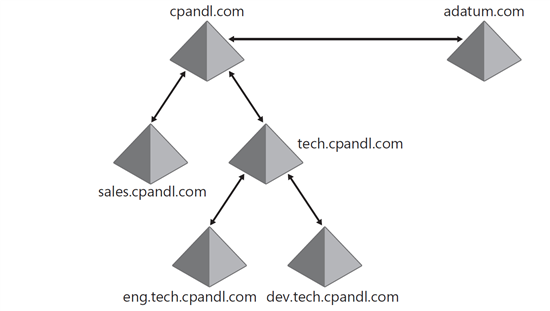
Figure 4-5 A domain forest with two domain trees
As an administrator, you create domain forests to reflect the structure of your organization. Domains operate independently in a forest , but they share a common schema . forest activates communication across member domains . Like domain trees , domain forests also have a root domain . The first domain to be created in a new forest is the root domain . The first domain to be built into each tree in the forest , asThe root domain is for that tree only . Figure 14-1 Cpandl.com and adatum.com two root domain for a tree on their own, but because Cpandl.com first domain is that the root domain is made, then the forest root domain is .
Figure 1-4 Expanding the Domain Environment
Note: Domains in a forest are linkedthroughabsolute two-way transitive trusts . Trust is a link between two domain where a domain called Trusting domain known to login authentication logon authentication to the domain that is the name of the trusted domain known as the catalog. Trust due to binding domains of parent and child in a domain tree the same as well as the action on the root of the domain tree. The standard protocol for the Trust used Krbrvs Version 5 Kerberos version 5 is . More information is given in Chapter Eight .
Forest functions are limited and controlled by the forest functional level . There are several forest functional levels available, including :
Windows 2000 supports the second version of Windows NT 4.0 and later. However, you cannot use the second Windows NT 4.0 controller with Windows Server 7, and you cannot use the second Windows Server 2 controller with Windows NT 4.0 servers .
Windows Server 2003 supports the second Windows Server 2 controller. When all domain in the forest with the fashion work, you will see improvements in the replication of the global catalog global catalog and operations efficiency replication for data’ll be Active Directory. That’s because Link Value Replication is used and you’ll see that intersite replication improves. You can class objects and attributes to the schema to disable the dynamic auxiliary class dynamic auxiliary classes to use, domainRename or one-way , two-way and transitive forest trusts create .
Windows Server 2008 supports the second Windows Server 2 controller. When all domain in the forest with the fashion work, you’ll improve the replication of intersite and intrasite outside the organization will be. The second controller can use Distributed File System – DFS for replication instead of File Replication Service – FRS , which improves recovery. In addition, security principals are not created until the PDC emulator on Windows Server 7 in the forest rootNot working. This is almost like a Windows Server 7 related need .
Note: As of this writing, when you launched the second Windows Server 2008 R2 controller, it also has anew forest functional level called Windows Server 2008 R2 . When the forest in this fashion, and all domain controllers Windows Server 2008 R2 , you have special features such as Deleted Object Recovery , Managed Service Accounts and Offline Domain Join is .
Organizational units – OUs
Organizational units Organizational units – OUs containers logical logical containers that are used to organize objects within a domain are used. This is because the OUs are the smallest sphere that you can authority of the authority delegated delegate , you can use OUs to manage admins about users, groups, and computers as well as for other resources such as printers and shared folders Use .
When the OUs to OUs Other add, you have a hierarchy in the domain you are creating. Because each domain in the domain forest has its own OUs hierarchy . Hierarchy of OUs in a domain independent of the other domain other is .
Ideally, you make things easy by making them. You can use the following to :
- Reflect Managed Resources and Accounts
- Reflect the structure of the branches within the organization
- Reflection of geographical locations and business units
- Reflect the value or value of centers within the organization
If you read this description, you may create OUs for any business unit or unit within the organization. This allows you to assign the level of managers, management authority to manage accounts and resources within the same business unit or department. If one of these managers in the future needs to have management authority for one business unit or another, you can assign that authority to that particular OU .
By default, all Ous of child from parent OUs licenses, permissions to inherit inherit them. For this reason, when an administrator is required to authorize a parent OU , the administrator can actually manage all the accounts and resources in the child OUs of that parent OU . For example, if North America is the parent OUs state, the United States and Canada are the child OUs , the administrators with authority for North America will automatically have the same powers for the OUs. In the United States and Canada will be .
15-1 in the form of domain names cpandl.com two OU named sales and services for global operations in North America , Europe and South America uses . sales and services are top-level OUs . Sales has three other nested OUs named NA , Europe and SA . Services has three other nested nested OUs Named NA , Europe and SA . In this environment, administrators can have different levels of management. Domain administrators are licensed for the domain and all of its OUs . Administrators Sales OU licensed for Sales and all nested OUs , but for the domain or Services OU and three nested OUs within it are not permitted. Inside Sales OU Administrators NA , Europe and SA only have licenses for the same OUs .
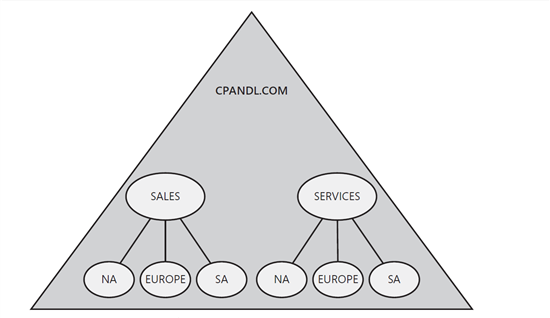
Figure 2-4 Organizational units within the domain

