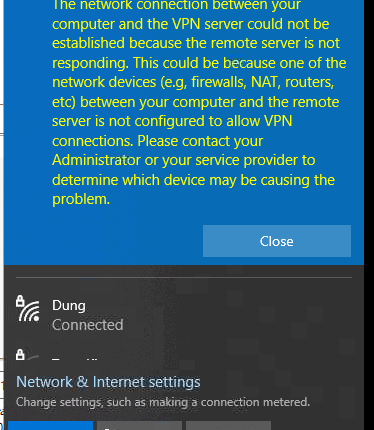
Due to disabling PPTP VPN support in iOS, one of my clients decided to reconfigure the VPN server running Windows Server 2012 R2 from PPTP to L2TP/IPSec. Internal VPN clients from inside LAN connect to the VPN server without any problems, however external Windows clients get the error 809 when trying to establish the connection with the L2TP VPN server:
In other Windows versions, the connection errors 800, 794 or 809 may indicate the same problem.
It is worth to note that the VPN server is behind a NAT, and the router is configured to forward L2TP ports:
- UDP 1701 — Layer 2 Forwarding Protocol (L2F) & Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
- UDP 500
- UDP 4500 NAT-T – IPSec Network Address Translator Traversal
- Protocol 50 ESP
These ports are also open in the Windows Firewall rules for VPN connection. Those, the classic configuration is used. The built-in Windows VPN client is used for connection.If you connect to the same VPN server via PPTP, the connection is successfully established.
VPN Error 809 for L2TP/IPSec on Windows behind NAT
As it turned out, the problem is already known and described in the article https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/kb/926179. The Windows built-in VPN client doesn’t support by default L2TP/IPsec connections through NAT. This is because IPsec uses ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload) to encrypt packets, and ESP doesn’t support PAT (Port Address Translation). If you want to use IPSec for communication, Microsoft recommends using public IP addresses on the VPN server.
But there is also a workaround. You can fix this drawback by enabling support for the NAT-T protocol, which allows you to encapsulate ESP 50 packets in UDP packets on port 4500. NAT-T is enabled by default in almost all operating systems (iOS, Android, Linux) except Windows.
If the L2TP/IPsec VPN server is behind a NAT device, in order to connect external clients through NAT correctly, you have to make some changes to the registry both on the server and client side to allow UDP packet encapsulation for L2TP and NAT-T support in IPsec.
- Open the Registry Editor (
regedit.exe) and go to the following registry key:- Windows 10/8.1/Vista and Windows Server 2016/2012R2/2008R2 — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent
- Windows XP/Windows Server 2003 — HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\IPSec
- Create a DWORD parameter with the name AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule and the value 2;
Note. Possible AssumeUDPEncapsulationContextOnSendRule values are:
- 0 – (a default value) suggests that the server is connected to the Internet without NAT;
- 1 – the VPN server is behind a NAT device ;
- 2 — both VPN server and client are behind a NAT.
Just restart your computer and make sure that the VPN tunnel is established successfully
Multiple L2TP VPN Connections from the same LAN
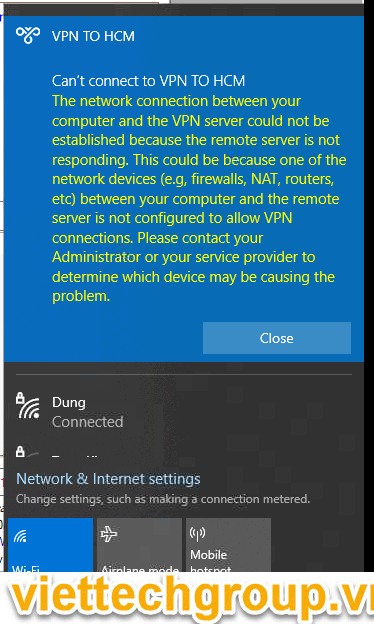
There is another interesting VPN bug. If your local network has several Windows computers, you cannot establish more than one simultaneous connection to an external L2TP/IPSec VPN server. If you try to connect to the same VPN server from another computer (with an active VPN tunnel from different device), error code 809 or 789 will appear:
Error 789: The L2TP connection attempt failed because the security layer encountered a processing error during initial negotiations with the remove computer.
Interestingly, this problem only occurs on Windows devices. On Linux/MacOS/Android devices on the same local network, there are no such problems. You can easily connect to the VPN L2TP server from multiple devices at the same time.
According to TechNet, the issue is related to incorrect implementation of the L2TP/IPSec client on Windows (not fixed for many years).
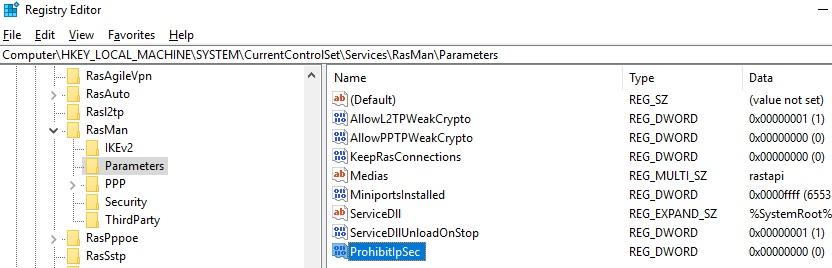
To fix this bug, you need to change two registry parameters in the HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\RasMan\Parameters registry key and restart your computer:
- AllowL2TPWeakCrypto – change to 00000001 (allows weak encryption algorithms, for L2TP/IPSec the MD5 and DES algorithms are used);
- ProhibitIPSec – change to 00000000 (enables IPsec encryption, which is often disabled by some VPN clients or system tools).
Run the following command to change apply these registry changes:
reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rasman\Parameters" /v AllowL2TPWeakCrypto /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f<br>reg add "HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\Rasman\Parameters" /v ProhibitIpSec /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f
This enables support for concurrent L2TP/IPSec VPN connections on Windows through a shared public IP address (works on all versions from Windows XP to Windows 10).
Source woshu
Phương Nguyễn